
The Risks of Welding Fume
According to the HSE welding fume guidance, risks from inhalation at low concentrations include respiratory irritation and asthma. At higher concentrations, risks range from metal fume fever through to poisoning or lung cancer. The HSE (UK Health & Safety Executive) states:
“By law you must protect your workers by controlling the health risks from welding fume. This applies to specialist welders and workers who do some welding, no matter how small the amount.”
For further information refer to the HSE website: Welding fume: protect your workers →

Control Measures for Welding Fume Risks
Whilst LEV (local exhaust ventilation) methods are often seen as the primary control method to reduce welding fume exposure, there is another way:
“Reduce and Control the Risk with Maxx® Gases”
Using welding techniques and materials that reduce fume exposure is a step up the hierarchy of controls to minimise risk. Maxx® welding gases produce lower levels of both particulate fume and ozone as well as additional productivity benefits.
Maxx® Gas – Minimal Fume
Extraction is not the sole solution to minimising the risks of welding fume, the correct choice of welding gas also plays a part to reduce fume generation at source. However, not all welding gases are equal. Maxx® welding gases were purpose-designed, in collaboration with The Welding Institute (TWI), to generate low levels of fume and ozone and thereby, reduce risk.
Whatever you are welding we have a Maxx® gas for you.
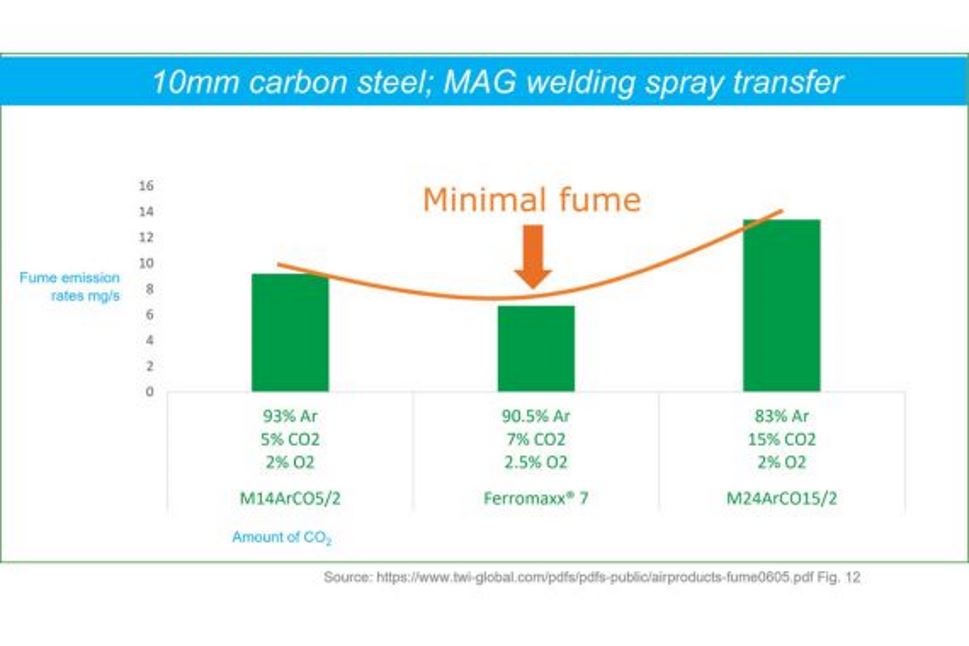
Carbon Steel Welding
Ferromaxx® gas provides a better working environment in terms of fume emission rates compared to conventional Argon/CO2 welding gas mixes coupled with improved productivity, high weld quality and fewer rejects.
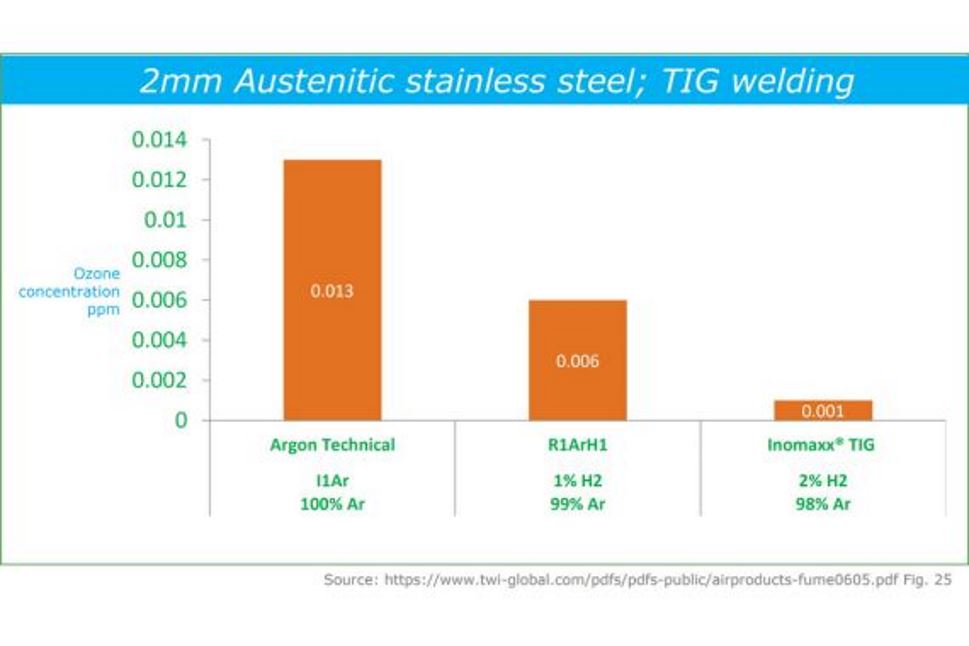
Stainless Steel Welding
Inomaxx® gas significantly generates significantly lower levels of ozone compared to Argon or conventional welding gas mixtures when welding stainless steel. Inomaxx® gas additionally produces noticeably cleaner, brighter welds and is easier to use.
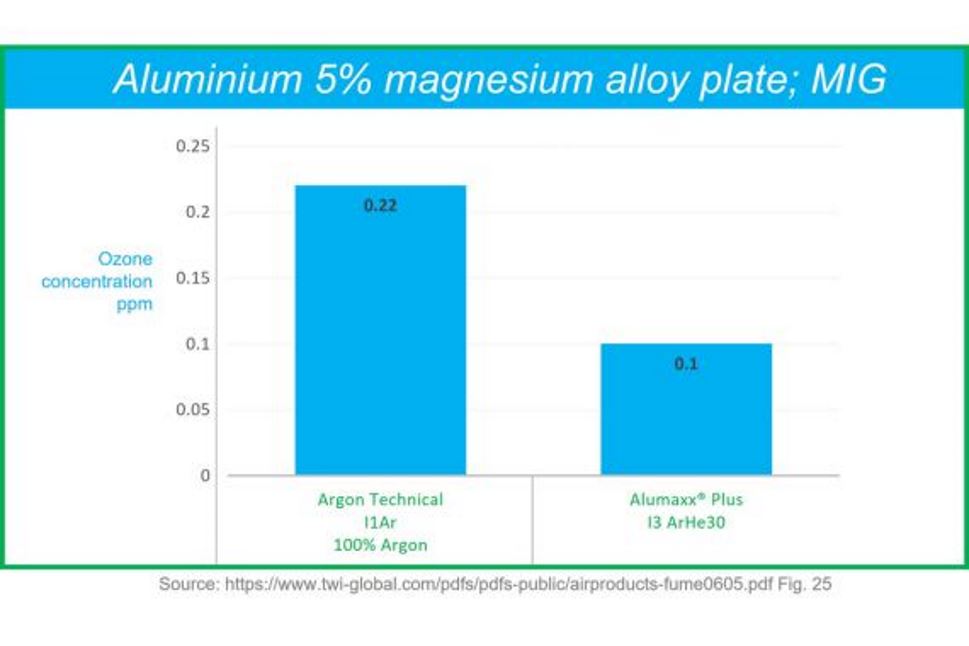
Aluminium Welding
Alumaxx® Plus gas dramatically increases both the workplace safety due to it’s very low levels of ozone production particularly when compared to the more frequently used alternative, Argon. An additional benefit is the significant increase in weld travel speeds, leading to higher productivity.


